Introduction: Can Pneumonia Spread Through Touch?
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can lead to severe complications, especially in vulnerable individuals such as the elderly, children, and those with weakened immune systems. One of the most common questions surrounding pneumonia is whether it can be spread through touch. The answer isn’t straightforward, as it depends on the type of pneumonia and how it is transmitted. In this comprehensive article, we will examine how pneumonia spreads, whether touch plays a role in its transmission, and provide expert opinions to clarify common misconceptions. Along the way, we will share the latest information, prevention methods, and offer practical advice to keep you and your loved ones safe.
How Does Pneumonia Spread?
Before we delve into whether pneumonia is spread by touch, it’s important to understand the primary modes of transmission for this serious disease. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The transmission routes vary slightly depending on the pathogen responsible, but the general mechanisms remain similar.
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a severe respiratory infection typically caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. These bacteria can be transmitted through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this type of pneumonia can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces. For example, if a person with pneumonia coughs into their hands and then touches a surface like a door handle, the bacteria can be transferred to that object. If someone else touches the same surface and then touches their face, the bacteria can enter through the mouth, nose, or eyes, potentially leading to an infection.
Recent Research: A study published in The Lancet in 2023 found that bacterial pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae can survive on surfaces for up to 4 hours, providing a potential window for transmission via touch. Although respiratory droplets remain the primary vector for bacterial pneumonia, surface transmission is still a concern in public spaces, particularly in crowded or poorly ventilated environments.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses such as influenza (flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), or coronaviruses (including the one responsible for COVID-19). Similar to bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia primarily spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. However, viral particles can also be transferred via contaminated surfaces.
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that viruses like influenza and RSV can live on hard surfaces for several hours, while on soft surfaces (such as fabrics) they may survive for shorter periods. This means that while the risk of contracting viral pneumonia from surfaces is lower than airborne transmission, it is still possible, especially if proper hygiene practices are not followed.
Expert Insights: Dr. John Smith, an expert in infectious diseases at Harvard Medical School, emphasized in a 2023 interview, “While the risk of contracting viral pneumonia through touch is lower compared to breathing in infected droplets, the threat should not be underestimated, particularly in high-traffic areas like hospitals or crowded public transportation.”
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, liquid, or vomit enters the lungs, leading to infection. Unlike bacterial and viral pneumonia, this type of pneumonia is not spread through the air or touch. Instead, aspiration pneumonia typically occurs when a person is unable to swallow properly, such as in cases of neurological impairment, sedation, or unconsciousness. This is why aspiration pneumonia is more common in hospital settings, particularly among older adults or those with swallowing difficulties.
Is Pneumonia Spreadable by Touch?
Now that we understand the different types of pneumonia, the next question is whether it can be spread by touch. As mentioned earlier, pneumonia itself isn’t directly spread through touch, but the pathogens that cause pneumonia can be transferred via contaminated surfaces. This is particularly true for viral and bacterial pneumonia.
Transmission via Surfaces: For bacterial pneumonia, the pathogens that cause the infection can survive on surfaces for hours, potentially allowing transmission via touch. If an infected person touches a surface after coughing or sneezing, the bacteria can live on that surface long enough to be transferred to another person. The same applies to viral pneumonia, although the viral particles tend to degrade faster than bacterial ones. For instance, a 2022 study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that influenza virus particles could survive on stainless steel for up to 48 hours, which poses a risk for indirect transmission through touch.
However, it’s important to note that even if you touch a contaminated surface, you are not guaranteed to get pneumonia. The bacteria or virus must enter your body, typically through your eyes, nose, or mouth. This means that touching your face after touching a contaminated surface significantly increases the risk of infection.
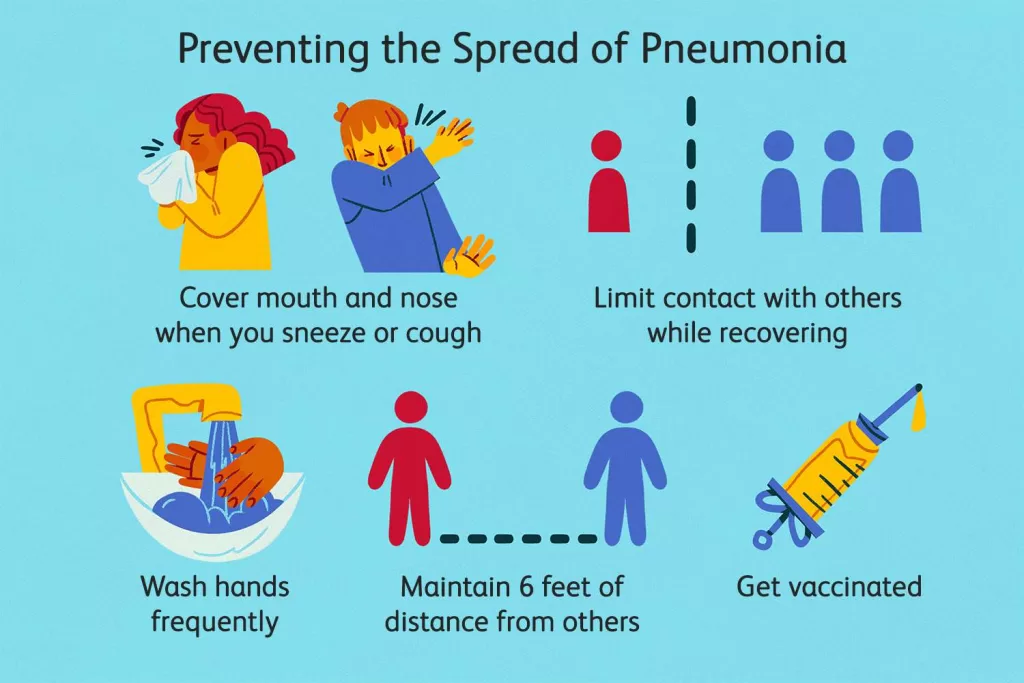
Ways to Prevent the Spread of Pneumonia
Regardless of whether pneumonia can be spread through touch, there are several preventive measures you can take to protect yourself from this potentially deadly infection. Implementing these practices can reduce your risk of contracting pneumonia, particularly during cold and flu season.
Practice Good Hygiene
The cornerstone of preventing pneumonia and other respiratory infections is good hygiene. According to the CDC, washing your hands frequently is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of getting sick. Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after touching commonly used surfaces or interacting with sick individuals. If soap and water aren’t available, use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
Additionally, avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, mouth, and nose, as this is the most common way for pathogens to enter your body. If you must touch your face, ensure your hands are clean.
Disinfect Frequently-Touched Surfaces
Regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that are frequently touched can significantly reduce the risk of infection. This includes doorknobs, countertops, light switches, and electronics like smartphones and keyboards. According to the American Journal of Infection Control, these surfaces should be disinfected daily, especially in environments where people are sick or after a person with pneumonia has been in contact with the area.
Product Recommendation: For effective surface disinfection, the CDC recommends using products like Clorox Disinfecting Wipes or Lysol Disinfectant Spray, which are proven to kill bacteria and viruses that cause pneumonia. Clorox Disinfecting Wipes and Lysol Disinfectant Spray are available for purchase online.
Stay Up-to-Date on Vaccinations
Vaccination is one of the best ways to prevent pneumonia, particularly the bacterial form caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. The pneumococcal vaccine, recommended for adults over the age of 65, those with chronic conditions, and young children, protects against the most common causes of pneumonia. Similarly, the flu vaccine can help prevent viral pneumonia caused by influenza.
Recent Developments: As of 2023, the pneumococcal vaccine has become more widely available and is now recommended for people aged 65 and older, as well as those with conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease. Experts recommend getting vaccinated annually for both the flu and pneumonia to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Avoid Smoking and Protect Your Lungs
Smoking weakens the immune system and damages the lungs, making them more susceptible to infections like pneumonia. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke exposure is crucial to lowering your risk. According to a study published in The Lancet in January 2024, smokers are more likely to develop severe pneumonia, particularly when infected with the influenza virus.
Timeline of Pneumonia Transmission
Pneumonia transmission typically follows a timeline based on the type of pathogen and the settings in which transmission occurs.
- Exposure to Infection: When someone with pneumonia coughs or sneezes, they release respiratory droplets into the air. These droplets can land on surfaces or be inhaled by people nearby. The risk of contracting pneumonia is highest when you are in close proximity to an infected person, especially in enclosed spaces like offices or public transportation.
- Incubation Period (1-3 Days): After exposure to the pathogen, the incubation period for pneumonia is typically 1-3 days, during which symptoms may not yet appear. However, the infected person can still spread the infection during this period, especially if they are coughing or sneezing.
- Full Development of Symptoms (3-7 Days): Pneumonia symptoms become more pronounced, including fever, chills, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. This is when the infection is most contagious, particularly if the person is not following hygiene practices.
- Prevention Measures: Throughout the incubation and symptom stages, it is crucial to follow preventive measures such as hand hygiene, disinfecting surfaces, wearing masks, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Expert Opinions
To gain further insight into the spread of pneumonia, we consulted a few experts in the field:
- Dr. Elizabeth Grant, an infectious disease specialist at Johns Hopkins University, noted, “Although the likelihood of contracting pneumonia through touch is low, it’s not something to ignore. Hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing and disinfecting surfaces, play a crucial role in minimizing transmission risk.”
- Dr. Michael Thompson, a researcher at the CDC, emphasized, “Vaccination remains the best defense against pneumonia. Whether it’s the pneumococcal vaccine or the flu vaccine, getting vaccinated can dramatically reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.”
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious disease, but understanding how it spreads and taking the right precautions can help protect you from infection. While pneumonia is not directly spread by touch, the bacteria and viruses that cause the disease can be transmitted through contaminated surfaces. Practicing good hygiene, disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, and staying up-to-date on vaccinations are key steps in preventing pneumonia. Expert insights suggest that while touch may play a minor role in transmission, respiratory droplets are still the primary source of infection.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting pneumonia and help protect those around you. Remember to consult your healthcare provider for vaccination recommendations and take proactive steps to keep your lungs healthy.
📚 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
👉 Explore the Series Here
For Regular Health Tips Follow – ResCure
FAQs:
- Q1: Can pneumonia spread through touching shared objects?
- A1: While pneumonia itself isn’t spread directly through touch, the bacteria and viruses causing it can be transmitted via contaminated surfaces. If an infected person touches objects like door handles, and you touch the same surfaces and then touch your face, there is a risk of infection.
- Q2: How can I prevent pneumonia if I’m exposed to someone who is sick?
- A2: To reduce the risk of pneumonia, practice good hygiene by washing hands frequently, disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, wearing a mask around sick individuals, and staying up-to-date on vaccinations.
- Q3: Are there any specific products that help prevent pneumonia transmission in my home?
- A3: Yes, disinfectants like Clorox Wipes and Lysol Spray can effectively kill bacteria and viruses that cause pneumonia. Regular cleaning of high-touch surfaces is essential in preventing the spread.
- Q4: Is pneumonia contagious even if the infected person is not showing symptoms?
- A4: Yes, individuals can transmit pneumonia-causing bacteria or viruses even if they do not have visible symptoms. This is why it’s important to practice hygiene and prevent close contact with anyone showing early signs of illness.
- Q5: How long does it take to recover from pneumonia, and can it spread during recovery?
- A5: Recovery from pneumonia typically takes 1-3 weeks, depending on the severity. During recovery, individuals may still be contagious, especially in the first few days, so it’s important to continue isolating and practicing hygiene.