Introduction: Vertigo Causes in Young Adults
Vertigo, a disorienting sensation of spinning or dizziness, can disrupt everyday life, particularly for young adults who may experience it under various circumstances. Understanding the multifaceted causes of vertigo is crucial for effective management and treatment. This in-depth exploration sheds light on the latest research, offers practical insights, and provides a timeline of key developments in the understanding and treatment of vertigo.
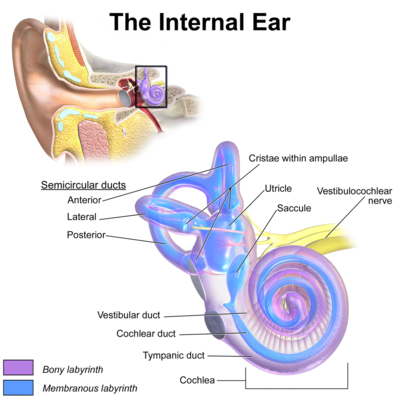
What is Vertigo? An In-Depth Look
Vertigo is distinct from general dizziness. It involves a specific sensation where an individual feels as if they or their surroundings are moving in a spinning motion. This condition is often related to disturbances in the inner ear or brain’s balance mechanisms. Vertigo can significantly impact a young adult’s daily activities, affecting their academic performance, work productivity, and overall quality of life. Recognizing and understanding vertigo’s unique nature helps in identifying effective treatments.
Common Causes of Vertigo in Young Adults
1. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is a prevalent cause of vertigo among young adults. It arises when calcium carbonate crystals in the inner ear become dislodged from their usual position and move into one of the semicircular canals. These canals are essential for maintaining balance. When the crystals move, they disrupt normal fluid flow, causing misleading signals to be sent to the brain, resulting in vertigo. BPPV can be triggered by specific head movements, such as turning over in bed or looking up. Treatment often involves the Epley maneuver, a series of head and body movements designed to reposition the dislodged crystals.
2. Vestibular Neuritis
Vestibular neuritis is an inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which plays a crucial role in balance and spatial orientation. This condition is typically caused by a viral infection, such as the common cold or flu. It manifests suddenly with severe vertigo, nausea, and balance difficulties. Unlike BPPV, vestibular neuritis is not triggered by specific movements but occurs abruptly. Treatment usually involves medications to alleviate symptoms and vestibular rehabilitation therapy to improve balance.
3. Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease, though more commonly diagnosed in older adults, can also affect young people. This chronic condition involves episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a sensation of fullness in the ear. The exact cause of Meniere’s disease remains uncertain, but it is believed to be related to an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the inner ear. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and may include dietary changes, medications, and in severe cases, surgical options to reduce inner ear fluid buildup.
4. Migrainous Vertigo
Migrainous vertigo, or vestibular migraine, is a type of vertigo linked with migraine headaches. It can occur with or without an accompanying headache. For young adults experiencing migraines, vertigo may also be a symptom. This form of vertigo is often associated with other migraine symptoms, such as light sensitivity and nausea. Management typically involves addressing the underlying migraine with medications and lifestyle changes.
5. Dehydration and Low Blood Pressure
Dehydration and sudden drops in blood pressure can also cause vertigo. For young adults, intense physical activity, inadequate fluid intake, or rapid changes in posture can contribute to these conditions. Dehydration reduces blood volume, which can lead to dizziness and vertigo. Ensuring adequate hydration and avoiding sudden posture changes can help manage these symptoms.
6. Anxiety and Stress
Mental health factors, including anxiety and stress, can manifest as physical symptoms such as vertigo. High levels of stress can affect the vestibular system, leading to dizziness and balance problems. Young adults undergoing significant life changes or dealing with high-stress environments are particularly susceptible. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, counseling, and lifestyle adjustments can be beneficial in alleviating stress-related vertigo.
7. Head Trauma
Head injuries or trauma can disrupt the inner ear or brain, resulting in vertigo. For young adults involved in contact sports or accidents, persistent dizziness following an injury should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Treatment may involve monitoring for concussion symptoms and rehabilitation for balance issues.
Diagnosis: Comprehensive Approach to Identifying Vertigo
Diagnosing vertigo involves a thorough assessment by a healthcare provider, which includes:
- Medical History and Symptom Evaluation: An in-depth discussion about the onset, nature, and triggers of symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: This may involve balance and eye movement tests to assess the vestibular system’s function.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans may be required to rule out structural abnormalities or other conditions.
- Vestibular Testing: Specialized tests, such as electronystagmography (ENG) or video head impulse testing (vHIT), assess inner ear and brain function related to balance.
Treatment and Management Strategies: Effective Approaches
1. Medications
Medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms of vertigo. For example, antihistamines like meclizine may help reduce nausea, while vestibular suppressants can alleviate dizziness. In cases like vestibular neuritis, corticosteroids might be used to decrease inflammation and improve recovery.
2. Physical Therapy
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT) is designed to help patients improve their balance and reduce dizziness through specific exercises. Techniques include gaze stabilization exercises, balance training, and habituation exercises to help the brain adapt to changes in the vestibular system.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing vertigo. Ensuring proper hydration, avoiding rapid positional changes, and managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises are effective strategies. For those with Meniere’s disease, dietary changes like reducing salt intake may help manage fluid levels in the inner ear.
4. Surgical Options
In rare cases where vertigo is caused by severe structural issues or intractable Meniere’s disease, surgical intervention may be considered. Procedures can include endolymphatic sac decompression or vestibular nerve section to reduce inner ear pressure and alleviate symptoms.
Recent Advances and Research: What’s New?
Recent advancements in the field of vertigo research have provided deeper insights into its causes and treatments. For instance, research conducted by Dr. Peter C. Read at the University of London has highlighted new approaches to vestibular rehabilitation therapy, improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the development of advanced imaging techniques has enhanced diagnostic accuracy, allowing for better-targeted treatments. Ongoing studies are also exploring the genetic and environmental factors contributing to vertigo, aiming to uncover more precise and personalized treatment options.
Timeline: Key Events and Developments
- 1992: The Epley maneuver, a key treatment for BPPV, is formalized by Dr. John Epley, significantly improving treatment outcomes for patients with vertigo.
- 2000: The American Academy of Otolaryngology publishes new guidelines for diagnosing and managing vestibular disorders, including BPPV and vestibular neuritis.
- 2010: Advances in imaging technologies, such as functional MRI, allow for better visualization of inner ear structures and contribute to more accurate diagnoses.
- 2015: The development of new vestibular rehabilitation techniques by Dr. Susan Herdman enhances treatment efficacy for patients with balance disorders.
- 2020: Research on the genetic basis of Meniere’s disease begins to provide new insights into potential personalized treatment approaches.
Expert Opinions: Insights from Leading Professionals
Dr. Susan Herdman, a renowned expert in vestibular rehabilitation, emphasizes the importance of tailored therapy for effective management. She notes, “Personalized vestibular rehabilitation therapy can significantly improve outcomes for patients with chronic vertigo, particularly when combined with lifestyle adjustments and stress management techniques.”
Dr. Peter C. Read, a researcher at the University of London, highlights recent advancements: “Innovations in imaging and understanding of vestibular disorders are paving the way for more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments, which are crucial for managing complex cases of vertigo.”
Dr. John Epley, the developer of the Epley maneuver, comments on the ongoing evolution of vertigo treatments: “The Epley maneuver remains a cornerstone of BPPV treatment, but ongoing research continues to refine and enhance its effectiveness.”
Conclusion: A Path to Managing Vertigo Effectively
Vertigo can be a challenging condition, particularly for young adults navigating various life changes. Understanding its causes, seeking accurate diagnosis, and exploring effective treatments are essential steps in managing this disruptive condition. With advances in research and treatment options, there is hope for improved quality of life for those affected by vertigo.
External Sources:
- Meniere’s Disease Research by National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders
- PubMed Article on Migrainous Vertigo
For Regular Health Tips Follow – ResCure
FAQs
Q1: What are the primary symptoms of vertigo in young adults?
The primary symptoms of vertigo in young adults include a sensation of spinning or dizziness, imbalance, nausea, and, in some cases, vomiting. These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be triggered by specific head movements or sudden changes in posture.
Q2: How can young adults differentiate between vertigo and other types of dizziness?
Vertigo specifically involves a spinning sensation, whereas other types of dizziness might involve lightheadedness or unsteadiness. Vertigo is often accompanied by balance issues and is usually related to inner ear disturbances.
Q3: What lifestyle changes can help manage vertigo in young adults?
Lifestyle changes that can help manage vertigo include staying well-hydrated, avoiding rapid posture changes, reducing stress through relaxation techniques, and maintaining a balanced diet. For those with BPPV, specific head maneuvers like the Epley maneuver can be beneficial.
Q4: Are there any specific exercises recommended for vertigo relief?
Yes, vestibular rehabilitation exercises are commonly recommended. These include gaze stabilization exercises, balance training, and habituation exercises to help the brain adapt to changes in the vestibular system.
Q5: When should a young adult seek medical attention for vertigo?
Medical attention should be sought if vertigo is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms like hearing loss, vision changes, or difficulty speaking. Immediate medical evaluation is crucial if vertigo follows a head injury or is associated with neurological symptoms.